IndexFiguresTables |
Kanan Bayramov and Seung Hyun JeonA Credit Card Based NFT Purchase DApp for Seamless Web3Abstract: There have existed transaction and connection difficulties between Web 2.0 and Web3 for a long time. Seamless Web3 has played a significant role to reduce the complexity of Web3 and the gap between Web2.0 and Web3. We propose a seamless Web3 based decentralized application (DApp) for non-fungible token (NFT) purchase by using credit cards. The proposed seamless Web3 DApp has been tested in an iOS system and shows positive results. The main goal is to connect Web 2.0 users purchase and store NFT within the DApp, without interacting with the complicated blockchain ecosystem such a wallet address, cryptocurrency or a crypto exchange account. Keywords: seamless Web3 , DApp , JNFT , Web3 wallet , cryptocurrency Ⅰ. IntroductionThe blockchain ecosystem has introduced a paradigm shift in managing financial transactions, ownership, and digital interactions, offering capabilities far beyond the traditional Web 2.0 environment. Known as Web3, this decentralized network has the potential to revolutionize industries by enabling secure, transparent, and unreliable transactions. However, Web3 adoption is hindered by significant challenges, including steep learning curves, complex user interfaces, and insufficient integration with traditional financial systems. Users often struggle with unfamiliar wallet setups, managing private keys, and navigating decentralized applications (DApps)[1], which alienate individuals lacking technical expertise. Privacy concerns, inconsistent documentation, and regulatory ambiguity further exacerbate these issues, deterring broader participation in Web3 ecosystems. One of the most pressing barriers is the lack of interoperability[2] between blockchain networks and traditional financial systems. Interoperability enables seamless data sharing, cross-chain communication, and transactions across networks but remains underdeveloped in most Web3 solutions. Setting up cryptocurrency wallets or accounts on blockchain exchanges involves multi-step processes that can overwhelm users. Additionally, limited integration between crypto exchanges and traditional financial systems restrictsthe use of cryptocurrencies for everyday activities, such as purchasing goods or engaging with Non-Fungible Token (NFT) marketplaces. NFTs are unique digital assets stored on blockchain technology, typically Ethereum, representing ownership of items such as art, music, or virtual goods. Unlike fungible cryptocurrencies, NFTs are distinct and non-replaceable, enabling creators to earn royalties but facing criticism for speculative values andtheenvironmental impact of blockchain's energy consumption. These challenges highlight the need for more accessible and user-friendly solutions to broaden Web3 adoption, called as seamless Web3. Recent advancements in blockchain infrastructure address these issues. Platforms like QuickNode simplify blockchain development with APIs for retrieving NFT data, Fireblocks offers enterprise-grade security and interoperability tools, and Reap integrates Web3 payment solutions using Fireblocks' robust infrastructure. Additionally, Mastercard’s Crypto Credential Program bridges Web 2.0 and Web3 by enabling secure cryptocurrency-to-fiat transactions. These innovations represent growing efforts to simplify blockchain interactions and improve accessibility for mainstream users. Building on these advancements, we propose a seamless Web3 DApp designed to bridge the gap between Web 2.0 users and the NFT marketplace. Leveraging QuickNode's NFT API for data handling, Fireblocks’ scalable infrastructure for secure operations, and Reap's user-focused design principles, the proposed DApp provides an intuitive platform for NFT purchases. Unlike traditional methods requiring blockchain expertise and crypto wallets, seamless Web3 DApp allows users to purchase NFTs using only their email address and credit card. Employing the ERC-1155 token standard via Thirdweb.com, the DApp ensures efficient operations, cost-effective transactions, and compatibility with multiple token types. The integration of oracle[3] facilitates interactions between off-chain payments and on-chain operations, delivering a seamless and user-friendly experience. By addressing barriers such as complexity, accessibility, and interoperability, the proposed solution aims to significantly lower entry barriers and democratize Web3 adoption for mainstream users. Ⅱ. Related Works2.1 Difference between Web3 and Web 3.0[1,4]The terms Web3 and Web 3.0 are often used interchangeably but represent two distinct visions in the evolution of the internet. While both aim to improve upon the current web (Web 2.0), they approach this transformation from different angles. Web3 focuses on decentralization and user empowerment through blockchain, whereas Web 3.0 centers around making the web smarter and more intuitive through semantic technologies and artificial intelligence. Web3 refers to a decentralized internet built on blockchain technology. It emphasizes user control, trust minimization, and peer-to-peer interactions. Originating from the blockchain and crypto communities, and first conceptualized by Ethereumco-founder Gavin Wood, Web3 seeks to reduce the control of centralized platforms by shifting power to users. Its core technologies include blockchain, smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. A major feature is that it enables users to own and manage their data and digital assets directly without relying on intermediaries. Key applications of Web3 include Decentralized Finance (DeFi), which offers financial services like lending and trading without banks (e.g., Uniswap, Aave), NFTs, which provide verifiable digital ownership (e.g., OpenSea), and Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs), which enable community-ledgovernance via smart contracts (e.g., MakerDAO). Wallets like MetaMask allow users to interact with these systems using cryptocurrencies, further enforcing the decentralized model. Economically, Web3 is driven by token-based models, allowing users to earn, spend, and trade crypto-assets natively within the ecosystem. Web 3.0, often linked to the vision of World Wide Web founder Tim Berners-Lee, is also referred toasthe Semantic Web. Its goal is to make web content more meaningful and machine-readable so that intelligent agents—powered by AI and machine learning—can understand, interpret, and act on information more effectively. Unlike Web3, which focuses on ownership and decentralization, Web 3.0 is about smarter automation and data interconnectivity. Web 3.0 technologies include artificial intelligence, big data, semantic metadata, and Internet of Things(IoT) connectivity. It promotes interoperability between systems and enables personalized, context-aware services. Examples of Web 3.0 applications include intelligent search engines like Google’s Knowledge Graph and Wolfram Alpha, personal assistants like Amazon Alexa and Apple Siri, and smart home devices like Nest thermostats. These systems learn from user behavior and data patterns to deliver smarter and more adaptive responses. While decentralization also plays a role in Web 3.0, it is lesscentral than in Web3. Comprehensively, both Web3 and Web 3.0 represent transformative visions for the internet’s future but tackle different aspects. Web3 reimagines the internet as a decentralized, user-controlled space where blockchain ensures transparency and autonomy. Web 3.0 envisions a more intelligent, interconnected internet where AI and semantics make content more accessible and useful. Understanding these differences is key as both paradigms continue to shape how we interact with the digital world. Table 1. Differences between Web3 and Web 3.0.
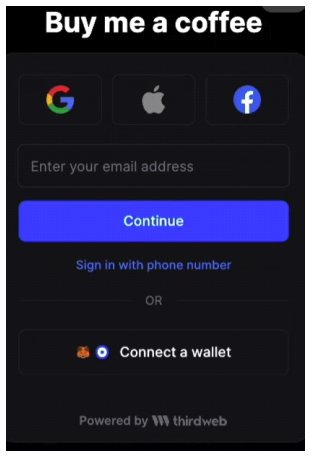
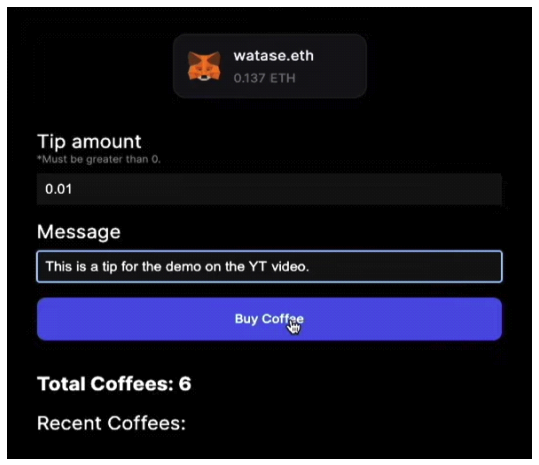
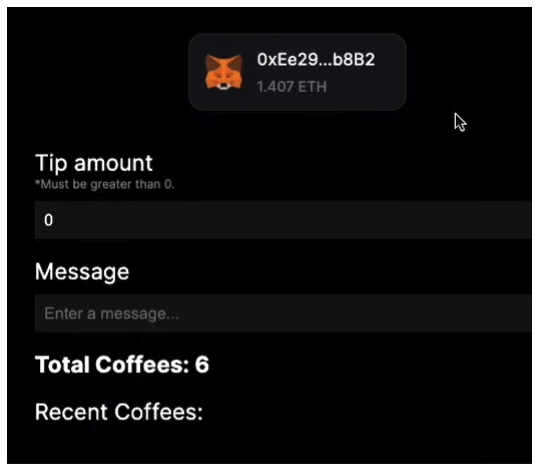
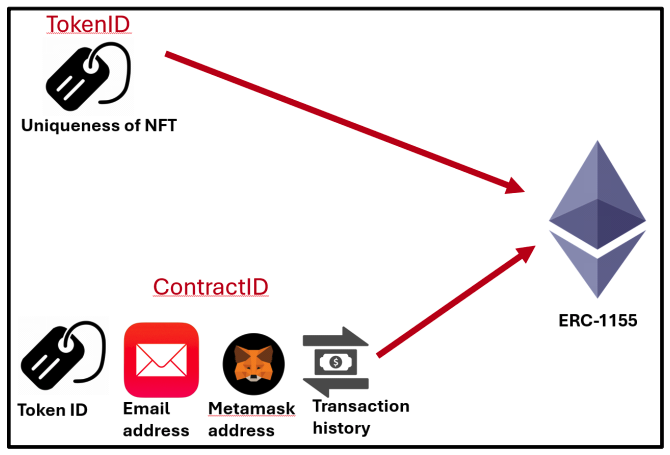
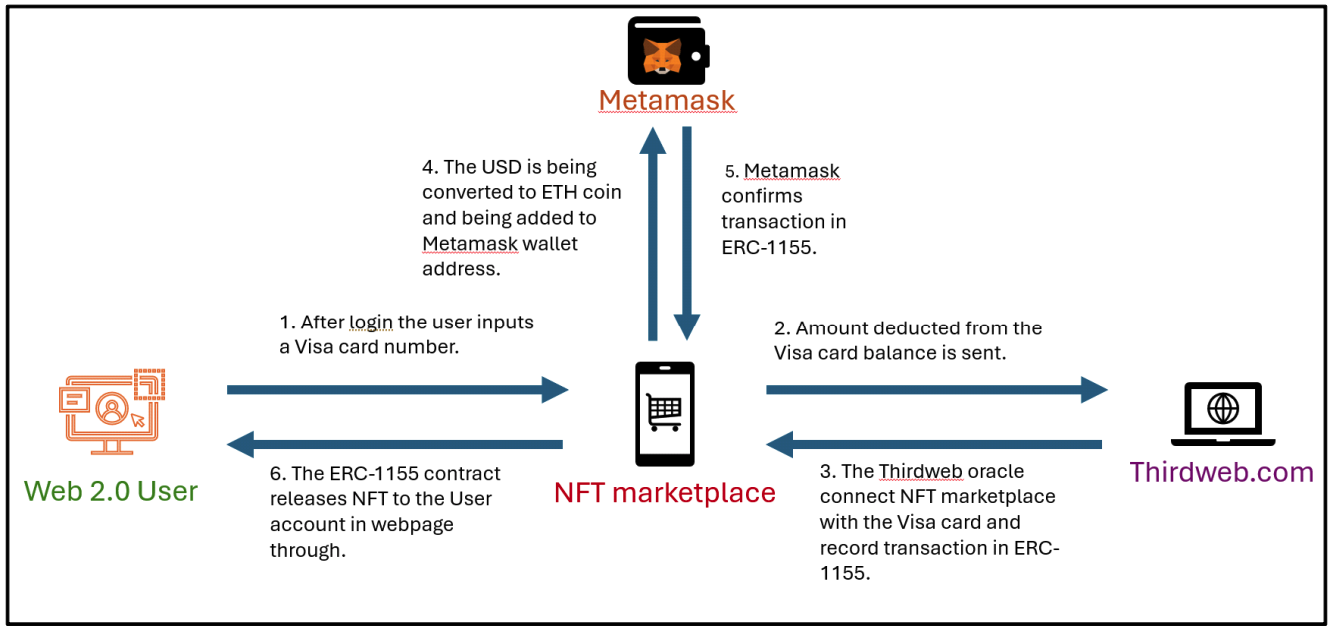
2.2 QuickNode APIQuickNode has become a vital infrastructure provider for Web3 projects, offering a wide range of APIs that simplify blockchain processes and enable smooth integration with Web 2.0 systems. Its NFT API[5] has proven transformative for NFT marketplaces by streamlining data retrieval, including creator information, ownership history, and transaction records across major blockchain networks like Ethereum, Polygon, and Solana. QuickNode's high-performance infrastructure ensures reliability, speed, and secure data handling, making it ideal for Web3 applications that prioritize user-friendly experiences. Additionally, its robust support for scaling and multi-blockchain compatibility makes it an invaluable tool for developers. This infrastructure played a pivotal role in developing the proposed seamless Web3 application for NFT purchases by abstracting blockchain complexities and enabling simplified interactions for end users. 2.3 Mastercard Crypto Credential ProgramMastercard’s Crypto Credential Program represents a significant step toward integrating traditional and decentralized financial systems. It provides secure, transparent cryptocurrency transactions and fiat currency conversion, bridging Web 2.0 and Web3 environments. The program primarily targets peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions[6], requiring intermediate blockchain knowledge that restricts accessibility for non-technical users. In contrast, the proposed seamless Web3 application for NFT purchases eliminates these barriers by supporting credit card-based transactions that are converted into cryptocurrency in real time. This approach removes the need for blockchain expertise, enhancing inclusivity and usability for a broader audience. Additionally, the app aligns with Mastercard’s vision of simplifying blockchain interactions while showcasing how traditional payment methods can adapt to decentralized technologies to achieve mainstream adoption. 2.4 Reap Corporate Cards and Fireblocks IntegrationReap’s shift[7] from traditional payment systems toWeb3 environments was facilitated by Fireblocks[8], which provided advanced tools like the Policy Engine for secure fund management and the Gas Station for enabling multi-blockchain interoperability. These features allowed Reap to manage digital assets efficiently and expand its services across multiple blockchains, including Ethereum, Tron, and Polygon. While Fireblocks is primarily designed for enterprise-level applications, its emphasis on security, scalability, and interoperability inspired the proposed NFT application. The DApp integrates Thirdweb.com for seamless blockchain deployment and employs the ERC-1155 token standard for batch NFT transfers, ensuring cost-effective operations and improved accessibility for non-technical participants. This strategic integration reflects Fireblocks’ principles, enabling the application to deliver a scalable and secure user experience tailored to individual users while addressing the unique challenges of Web3 adoption. 2.5 Integration of Web 2.0 Applications into the Existing Seamless Web3The seamless Web3 application for NFT purchases builds upon the foundational technologies and methodologies outlined in the related works. QuickNode’s NFT API shaped the app’s simplified data retrieval processes, ensuring efficient access to key information while maintaining high performance. Fireblocks influenced the app’s focus on scalability, security, and multi-blockchain compatibility, while Reap’s user-centric design principles guided the creation of an intuitive interface that caters to non-technical users. Furthermore, the application aligns with Mastercard’s efforts to bridge blockchain and traditional financial systems by enabling seamless, credit card-based NFT transactions. By synthesizing advancements from these systems, the application addresses Web3’s core challenges of accessibility, interoperability, and complexity. This innovative integration of cutting-edge technologies positions the app as a trail blazer in decentralized finance, driving broader adoption of Web3 solutions and redefining how traditional and decentralized systems interact. 2.6 Similar Cases: Buy Me a Coffee Web3 App[9]This application facilitates tipping exclusively through blockchain transactions, eliminating the need for traditional card payments. Users must possess a cryptocurrency wallet address to send tips. The system is built upon the ERC-20 standard, simplifying transaction processes within the Ethereum blockchain and its associated sidechains, such as Sepolia. This design choice ensures streamlined operations without the necessity to interact with other blockchain networks. Users can log in using their iCloud or Gmail accounts; however, to send tips, they must connect their cryptocurrency wallets. Due to the absence of seamless Web3 integration, this application is primarily suitable for individuals already experience in the Web3 ecosystem. After connecting their cryptocurrency wallet, users are prompted to enter the desired tip amount and have the option to include a personalized message for the recipient. Additionally, users must cover the applicable gas fees associated with their chosen network. The final section of the interface provides a summary of the total number of tips sent, enabling users to monitor their tipping activity. Upon initiating a transaction, the application confirms its functionality by processing the tip through the blockchain network. Notably, the application does not require extensive development efforts associated with blockchain interoperability, such as connecting disparate blockchain networks or integrating with various systems using blockchain oracles to bridge Web3 and Web2 applications. 2.7 Similar Cases: Towards Web3 Application[10]In developing our credit card-based NFT purchase DApp, a comprehensive examination of existing approaches and frameworks is essential. Among relevant works, Yu et al. proposed a significant contribution through their framework, WebttCom, designed explicitly to facilitate a seamless transition from Web2 to Web3 applications, particularly targeting enterprise-level integration. WebttCom introduces a robust three-layer architecture composed of a blockchain layer, a backend interpreter, and integration with existing Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms. Specifically, the blockchain layer leverages smart contracts for managing data provisioning, storage (public and private), and access control, ensuring data integrity and decentralized trust. Their backend interpreter acts as middleware, translating requests between traditional Web2 systems and blockchain-based Web3 backends, which considerably simplifies the complexity faced by developers unfamiliar with blockchain technologies. The integration with widely used Web2 platforms, like ServiceNow, demonstrates practicality and applicability to established business processes. Furthermore, WebttCom emphasizes automated API generation and extensive documentation to enhance developer productivity. Its effectiveness was validated through quantitative performance evaluations and qualitative surveys involving 1,000 industry practitioners, affirming the framework's ability to ease Web3 transitions efficiently. While WebttCom primarily addresses enterprise use cases focusing on backend integration, security, and data privacy, our proposed solution extends these foundational ideas towards a consumer-centric approach. Our NFT purchase DApp simplifies blockchain interactions by enabling mainstream consumers to utilize familiar payment methods such as credit cardsfor acquiring NFTs, abstracting the complexities of cryptocurrency wallets and blockchain interfaces. The distinction lies in our DApp's focus on ease-of-use, seamless fiat-to-crypto transactions facilitated by ERC-1155 token standards, and integration of intuitive front-end interfaces powered by QuickNode API, Fireblocks, and Reap platforms. Thus, our work leverages and builds upon WebttCom's principles of reducing Web3 complexity, translating them into a direct consumer-facing solution designed to accelerate mainstream adoption of blockchain technologies. Ⅲ. System ModelSeamless Web3 applications have emerged as a vital innovation to bridge the gap between traditional Web 2.0 and decentralized Web3 environments. These apps simplify blockchain interactions, allowing users to access blockchain-based services without needing extensive technical knowledge. After a major update to blockchain infrastructure in 2023, seamless Web3 solutions gained widespread popularity, enhancing user experience and accelerating the adoption of blockchain technologies. Our proposed seamless Web3 NFT purchase DApp aims to provide users with a simple, efficient method for purchasing NFTs, eliminating the complexities traditionally associated with blockchain transactions. The seamless Web3 NFT purchase DApp will be developed using Thirdweb.com, an open-source development environment that enables rapid deployment of blockchain applications. Specifically, we will utilize the “Edition Drop” contract offered by Thirdweb.com, which leverages the ERC-1155[11] token standard. ERC-1155 is ideal for the DApp because it offers several advantages, including: · Efficient Operations: Enables multiple operations within a single blockchain transaction. · Versatility: Supports both fungible and non-fungible tokens, providing flexibility in token design. · Storage Optimization: Requires less storage on the blockchain, reducing transaction costs. · Batch Transfers: Allows transferring multiple NFTs in a single transaction, improving efficiency. · Localization Support: Facilitates multi-language interfaces, enhancing usability for a global audience. Using the ERC-1155 standard in Table 2 ensures a seamless connection between credit card transactions and MetaMask wallet addresses. The smart contract will maintain TokenIDs of three NFTs, while the ContractID will store the app's MetaMask address. Additionally, contractArgs will encompass critical details such as TokenIDs, email addresses, and card transaction information, ensuring smooth integration with the blockchain ecosystem in Fig. 1. However, due to certain limitations within the Thirdweb.com environment, we are unable to directly link the user’s MetaMask wallet during deployment. To address this, a paper wallet address will first be generated to register the NFT address of the app. This intermediary step facilitates linking the NFTs with the user’s wallet, bridging the gap between deployment constraints and user interaction. The application will operate on Ethereum’s Sepolia Testnet[12], a blockchain network specifically designed for testing smart contracts and decentralized applications in a secure environment. The ERC-1155 contract will be written in Solidity, a programming language widely used for developing Ethereum-based smart contracts due to its optimization and compatibility with blockchain networks. On the front-end, we will use Next.js[13] alongside React.js[14] libraries, ensuring the app is responsive, intuitive, and accessible for users with limited blockchain experience. These technologies will enable the creation of a dynamic and seamless user interface. Table 2. Differences among ERC-20, 721 and 1155.
The app’s front-end design is tightly integrated with its blockchain infrastructure to provide a functional and user-friendly experience. This integration eliminates the complexities traditionally associated with blockchain applications, making NFT purchases straightforward for non-technical users. Additionally, the choice of Next.js ensures efficient server-side rendering, improving app performance and reducingloading times. React.js enhances the interactivity and responsiveness of the interface, enabling a smooth and engaging user journey. Together, these tools contribute to the app’s ability to combine advanced blockchain functionality with a user- centered design, paving the way for broader Web3 adoption. with practical usability, positioning the app as a scalable solution for future DApps. A Web3 oracle[15] will play a critical role in ensuring smooth interaction between off-chain and on-chain environments, providing real-time, reliable access to external data. In Web3, an oracle is a trusted intermediary that retrieves and verifies external information and delivers it to smart contracts on the blockchain. This DApp will utilize oracles to bridge the gap between Web 2.0 and Web3, ensuring seamless dataflow and enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of transactions. Oracles will connect the NFT marketplace with credit card transactions, offering a friction less experience for users unfamiliar with blockchain processes. The NFT prices will be displayed in fiat currency(USD) within the DApp to enhance usability for Web 2.0 users. When a user initiates a purchase using their email address and credit card information, the corresponding amount will be automatically converted into Tether cryptocurrency (called as USDT). The USDT will then be converted into ETH at the point of transfer and added to the Metamask wallet, ensuring seam less integration with blockchain operations. This process abstracts the complexities of cryptocurrency handling from the end user, providing a simple and intuitive purchasing experience. The seamless Web3 NFT purchase DApp offers an innovative solution for simplifying NFT transactions by integrating Web 2.0 payment methods with Web3 blockchain operations. Through using of the ERC-1155 token standard and the Thirdweb.com development environment, the app will provide an intuitive user experience, enabling credit card transactions to be seamlessly converted into cryptocurrency. By leveraging the Sepolia Testnet for testing, the DApp ensures smooth operation before transitioning to the main Ethereum network. Additionally, the integration of oracles ensures accurate, real-time data transfer, enhancing the app's usability. While open-source platforms present security challenges, the DApp will prioritize security best practices to mitigate risks and deliver a secure, efficient platform for NFT purchases. This DApp has the potential to play a significant role in driving the adoption of seamless Web3 solutions, bridging the gap between traditional and decentralized systems, and expanding the usability of blockchain technology for everyday users. Table 3. Comparison of the proposed DApp and the conventional solutions.
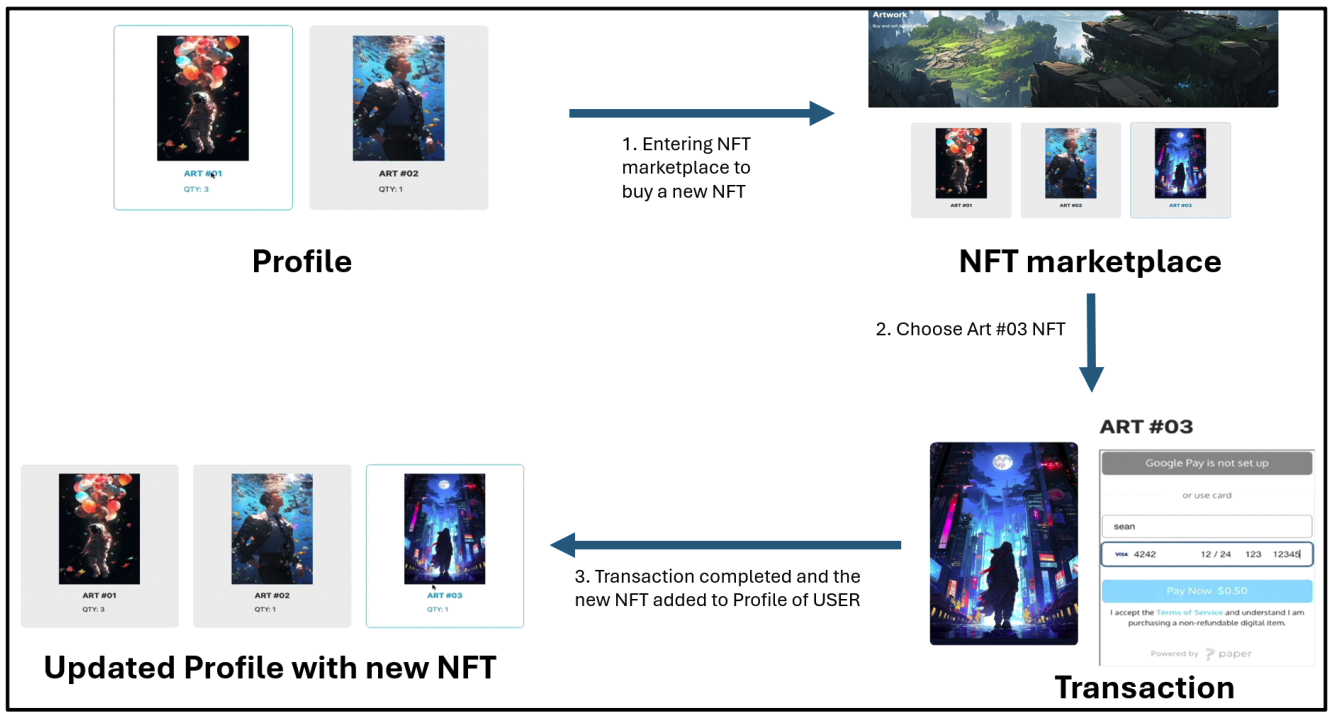
Ⅳ. DemonstrationThe NFT purchase application demonstrates a structured and seamless integration of blockchain technology with a user-friendly interface, enabling users to buy NFTs using credit cards. The process begins on the homepage, where users are required to enter their email address to create an account. This step is mandatory as the application stores purchased NFTs securely within the user’s account. After successful account creation, users can log in to access the marketplace, which features three distinct NFT options. Users select their desired NFT and specify the quantity they wish to purchase, with the price conveniently displayed in real-world currency for clarity and simplicity. To finalize the purchase, users enter their credit card details, which are securely processed by the application. The specified real-world currency amount is converted into cryptocurrency using the Sepolia Ethereum test network[16], ensuring a smooth and automated transition between fiat currency and blockchain transactions. The equivalent cryptocurrency amount is then transferred to the app's MetaMask wallet, which acts as an intermediary. At this stage, the application communicates with the Ethereum blockchain through a Web3 oracle. The oracle serves as a bridge between off-chain systems and the decentralized blockchain, enabling secure and reliable transaction execution. The Web3 oracle interacts directly with the smart contract, which is written in Solidity and deployed on the Ethereum blockchain. The smart contract holds critical data, including the NFT addresses, user wallet addresses, and transaction records. Upon confirming the cryptocurrency payment in the MetaMask wallet[17], the smart contract verifies the transaction details. Once validated, the smart contract releases the purchased NFT to the user’s account. Each transaction is recorded immutably on the blockchain, ensuring transparency, security, and traceability of NFT ownership. This application leverages blockchain technology to enhance security, decentralization, and trust while maintaining accessibility through the integration of conventional payment methods. The use of the Ethereum blockchain and a Web3 oracle ensures real-time interaction and reliable transaction execution. The MetaMask wallet facilitates cryptocurrency storage and blockchain communication, serving as a secure intermediary. The applications. Its ability to bridge traditional and decentralized systems makes it a valuable tool for broadening Web3 adoption. In Table 3, we describe the comparison of the proposed NFT purchase based DApp and the existing solutions, already mentioned before Sections. Ⅴ. DiscussionThe application was developed and run on the iOS system[18] using a MacBook, which offered a smooth development environment. However, challenges arose when attempting to run the DApp on a Windows system's local host, primarily due to differences in the package managers used: Yarn[19] on iOS and npm on Windows. These package managers have distinct characteristics, which contributed to the compatibility issues. Yarn, developed by Facebook, is renowned for its improved speed, enhanced security, and reliable dependency management. It installs packages in parallel, making it faster than npm, which installs packages sequentially. Although npm, the default package manager for Node.js[20], has narrowed the speed gap in recent versions, Yarn remains faster in certain use cases. Yarn also employs checksums to verify the integrity of every installed package before execution, ensuring higher reliability. Although npm has introduced security features like package audits, Yarn’s practices are still considered more robust. Furthermore, Yarn offers unique features such as Plug’n’Play (PnP), zero installs, and a built-in license checker, although these require more disk space compared to npm. Yarn’s PnP feature eliminates the traditional node_modules directory, instead storing dependencies in a single compressed file accessed through a virtual filesystem. This reduces disk usage, improves performance, and enhances security by preventing unauthorized packages from accessing undeclared dependencies, ensuring stricter dependency constraints. Table 4. Differences between Yarn and npm package managers.
The choice between Yarn and npm[21] ultimately depends on project requirements and workflow preferences. However, this application, which leveraged Thirdweb.com services, relied heavily on Yarn, creating compatibility challenges when transitioning to npm-based systems like Windows. Additionally, the iOS’s ecosystem provides better compatibility with tools like Yarn, which are widely supported in blockchain development. By contrast, Windows systems often face limitations in package manager availability and support, making them less equipped for blockchain development. Another factor contributing to the preference for the iOS is its ability to handle blockchain development's robust package management needs. Developers often prefer an iOS for its seamless integration with advanced tools and superior development environments, enabling faster and more reliable builds. While Windows is widely used, its ecosystem lacks the refinement and compatibility offered by the iOS in the blockchain domain. These factors collectively explain why the iOS remains the preferred choice for blockchain engineers, highlighting the challenges faced when adapting this DApp for use on Windows systems. Ⅵ. ConclusionThis paper introduces a Web3 application bridging traditional Web 2.0 payments with blockchain-based NFT marketplaces. By leveraging QuickNode, Fireblocks, ERC-1155 tokens via Thirdweb.com, and oracles for secure off-chain/on-chain communication, the proposed seamless Web3 DApp enables NFT purchases with just email and credit card details, eliminating crypto wallet complexities. Its intuitive design ensures accessibility for non-technical users. Highlighting the iOS's advantages in blockchain development, the DApp demonstrates a scalable, secure solution to democratize Web3 adoption, expanding blockchain usability for the conventional Web2.0 users. BiographyBiographyReferences
|
StatisticsCite this articleIEEE StyleK. Bayramov and S. H. Jeon, "A Credit Card Based NFT Purchase DApp for Seamless Web3," The Journal of Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences, vol. 50, no. 9, pp. 1486-1496, 2025. DOI: 10.7840/kics.2025.50.9.1486.
ACM Style Kanan Bayramov and Seung Hyun Jeon. 2025. A Credit Card Based NFT Purchase DApp for Seamless Web3. The Journal of Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences, 50, 9, (2025), 1486-1496. DOI: 10.7840/kics.2025.50.9.1486.
KICS Style Kanan Bayramov and Seung Hyun Jeon, "A Credit Card Based NFT Purchase DApp for Seamless Web3," The Journal of Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences, vol. 50, no. 9, pp. 1486-1496, 9. 2025. (https://doi.org/10.7840/kics.2025.50.9.1486)
|